Synthetic vs. Natural: What’s Really in Your Perfume?
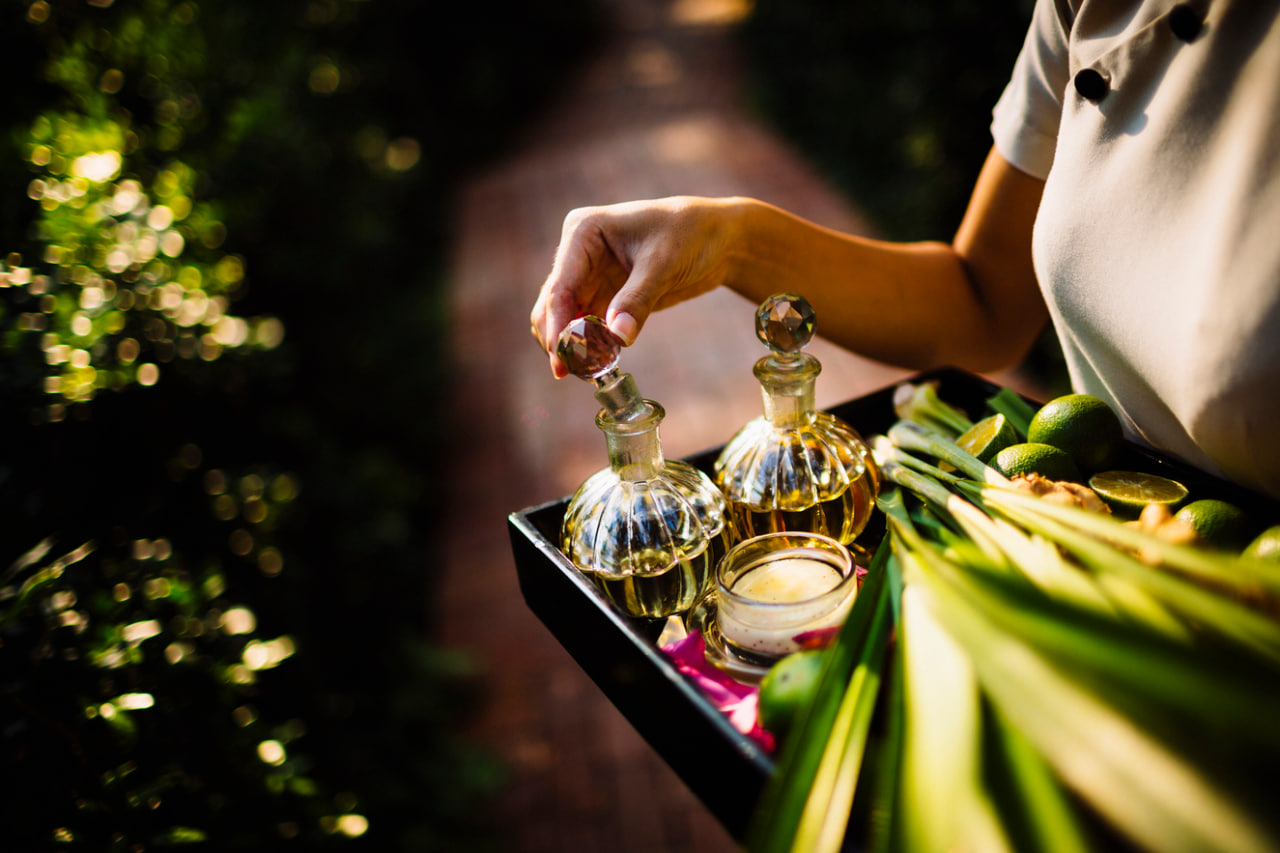
Perfumes are complex mixtures of aromatic compounds designed to evoke emotion, memory, and personal identity. When choosing a fragrance, many people wonder about the ingredients—specifically, the difference between natural and synthetic components. Understanding what goes into your perfume can help you make informed choices based on your preferences, sensitivities, and values. This blog explores the distinctions between synthetic and natural ingredients in perfumery, their roles, benefits, challenges, and the evolving landscape of fragrance creation.
What Are Natural Ingredients in Perfume?
Natural ingredients are sourced directly from plants, animals, or minerals. They include essential oils, absolutes, resins, and extracts obtained through various extraction methods such as steam distillation, solvent extraction, or cold pressing. Common natural ingredients include rose oil, jasmine absolute, sandalwood, vanilla bean, and ambergris (a rare animal-derived resin).
Natural ingredients often carry complex and nuanced scent profiles because they contain hundreds of chemical compounds. These rich, multi-layered aromas contribute to the depth and character of traditional perfumes. Additionally, natural materials are sometimes valued for their historical and cultural significance, connecting modern perfumery to ancient traditions.
What Are Synthetic Ingredients in Perfume?
Synthetic ingredients are artificially created compounds produced through chemical processes in laboratories. They mimic or enhance natural scents, or create entirely new fragrances that do not exist in nature. Examples include synthetic musks, vanillin (which mimics vanilla), and aldehydes (which add a sparkling quality).
Synthetic molecules offer perfumers unprecedented creative freedom. They can replicate rare or endangered natural ingredients, improve scent stability, increase longevity on the skin, and reduce allergic reactions caused by some natural components. Because synthetics can be produced consistently and in large quantities, they are more accessible and often more affordable.
Advantages of Natural Ingredients
One of the main appeals of natural ingredients is their authenticity and complexity. Perfumes made with high-quality natural oils often have a warm, rich character that synthetic materials can struggle to replicate fully. Many natural ingredients are also celebrated for their therapeutic or aromatherapeutic benefits, such as lavender’s calming effects or frankincense’s grounding aroma.
Natural ingredients are renewable resources when sustainably harvested, and they align with consumer desires for organic and eco-friendly products. For many consumers, natural perfumes represent purity, tradition, and connection to the earth.
Advantages of Synthetic Ingredients
Synthetic ingredients allow for greater consistency and creativity. Natural materials can vary significantly depending on climate, harvest time, and extraction methods, which can affect scent quality and availability. Synthetics ensure that a perfume smells the same with every bottle and batch.
They also enable the creation of scents that are otherwise impossible or unethical to produce, such as synthetic animalic notes that replace rare or protected animal substances. Synthetic molecules can extend the longevity and projection of a fragrance, making perfumes last longer on the skin.
Additionally, synthetic ingredients can reduce costs and make perfume more accessible to a broader audience.
Challenges and Considerations
Both natural and synthetic ingredients come with challenges. Natural materials can be allergenic, expensive, and subject to supply limitations due to environmental factors or overharvesting. Their complexity sometimes makes it difficult to isolate specific scent notes, leading to batch variability.
Synthetic ingredients, while consistent and versatile, sometimes face criticism for being “artificial” or less desirable. Some consumers worry about potential health effects, although most synthetic compounds used in perfumery are rigorously tested for safety.
There is also the question of environmental impact. While synthetics reduce pressure on natural resources, their production can involve petrochemicals and generate waste. On the other hand, unsustainable harvesting of natural materials can harm ecosystems and biodiversity.
The Modern Perfumer’s Approach
Today’s perfumers often blend natural and synthetic ingredients to achieve balanced, innovative fragrances. The goal is to combine the authenticity and depth of naturals with the versatility and stability of synthetics. This hybrid approach allows for greater artistic expression, sustainability, and accessibility.
Many niche and luxury brands emphasize natural ingredients, while mainstream perfumes rely heavily on synthetics for mass production. However, consumer awareness is growing, and demand for transparency and eco-consciousness is influencing ingredient choices across the industry.